See also
Sigma TXL index page
River Wye
Regents Canal
Wey Navigation
They say Bradford-on-Avon near Bath is one of England’s prettiest historical towns. I blundered through the other evening trying to outwit the satnav, and it didn’t look too shabby. With something to pick up near town, I wondered if the Avon river was paddleable, and found Andy Ballard’s nice canoeing vid above. He describes an 8-mile-loop which follows thne river towards Bath, before hopping up onto the parallel and lock-free Avon & Kennet canal at the Dundas viaduct to return to BoA. That will do nicely.
‘Pay attention at the back!’
Completed around 1810 towards the end of the ‘Canal Mania’, the Kennet & Avon Canal essentially crossed southern England’s watershed to link the then key port of Bristol at the mouth of the Avon with London on the Thames. At Paddington in London, the Grand Union was completed around the same time, and led up to the north’s mines, foundries and mills, and where the network of canals became much denser (below right).


The Thames and Avon rivers were long navigable inland as far as Bath and Reading and the K&A linked those two towns over 87 miles. Kayaking the Wey Navigation and packrafting London’s Regents Canal taught me that Britain’s canals helped kick off the world’s first industrial revolution. They linked or added to long-established river navigations to extend inexpensive and reliable cross-country transportation of heavy, bulky or fragile commodities.
At this time the decrepit road network along ther Bath Road (A4) was still suffering from 1500-years of neglect following the Roman era. Coaches carried passengers and packhorse trains were superior to wheeled carts, but turnpike fees (tolls to help pay for road upkeep) made them costly. Hostilities with France included attacks on coastal shipping in the English Channel, necessitating secure inland transportation to help provision the war effort. The former Wey-Arun Navigation linking London and Surrey’s gunpowder mills with the navy fleet at Portsmouth was another example.

Once 18th-century nimbyism had been overcome, canals soon became a reliable investment opportunity which made nearly all shareholders richer, while seeing commodity prices drop for all. But Britain’s canal boom was short lived and 30 years after completion, the K&A was trounced by the Great Western Railway, itself trounced a century later by the M4 motorway.
Since WW2 canals and their adjacent towpaths have been widely restored and especially in cities, can be historically interesting byways. But recreationally they’re more suited to walkers, cyclists and powered river craft than paddlers. The lack of a current means they can work both ways, but portaging locks can break a journey’s flow, as they can on a rivers like the Thames, where canoe chutes are few. And the popularity of canals and towpaths can make them busy places compared to a natural river winding through the landscape, with the odd aerated riffle to spice things up.
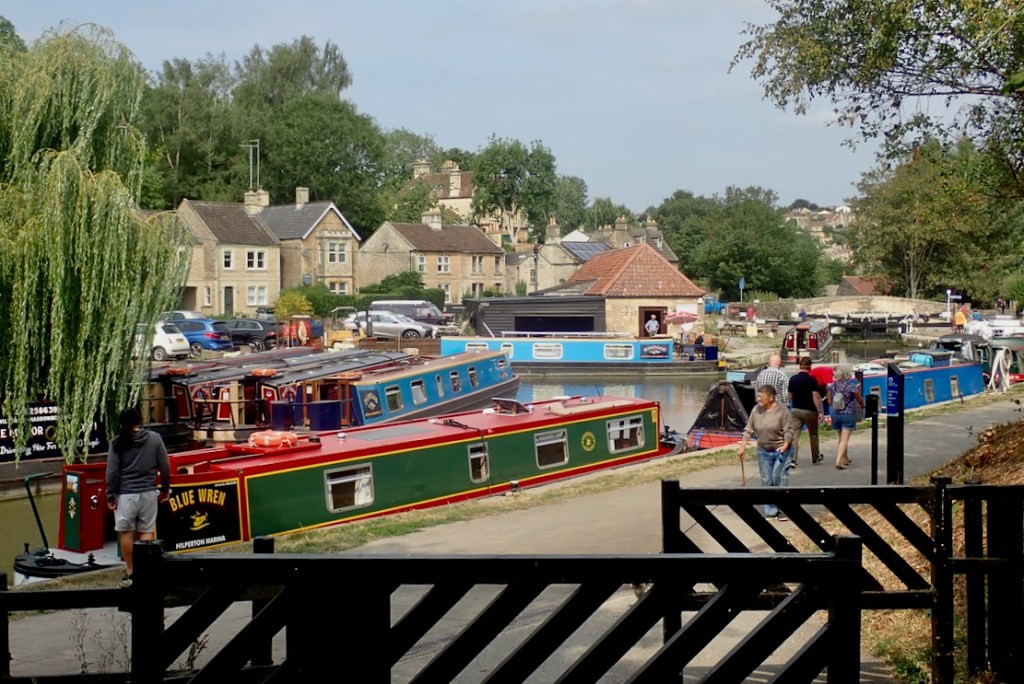





Signboard in the car park noting the dawn of rubberised fabrics in 1848 (interesting BoA Museum page) and which became Dupont hypalon we know and love, and then PVC. It explains the brand name of Avon Rubber Company and their RIBs (middle) and moto tyres (right). The factory was by the secind weir at Limpley. Avon RIBs were bought by French Zodiac in the 1990s, and after 112 years the Avon tyre factory up river in Melksham closed in 2023.



Soon I pass under the Avoncliff aqueduct which I’ll be crossing in a few hours.
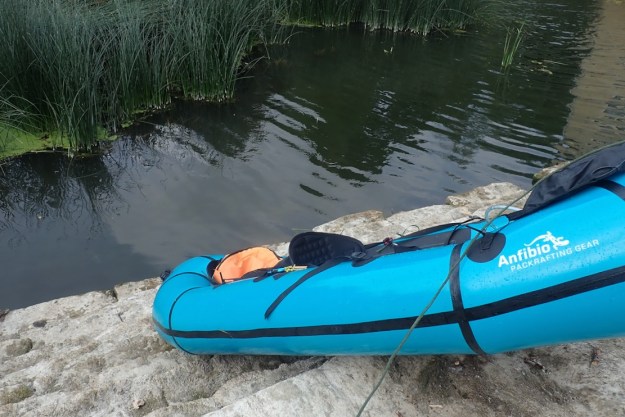
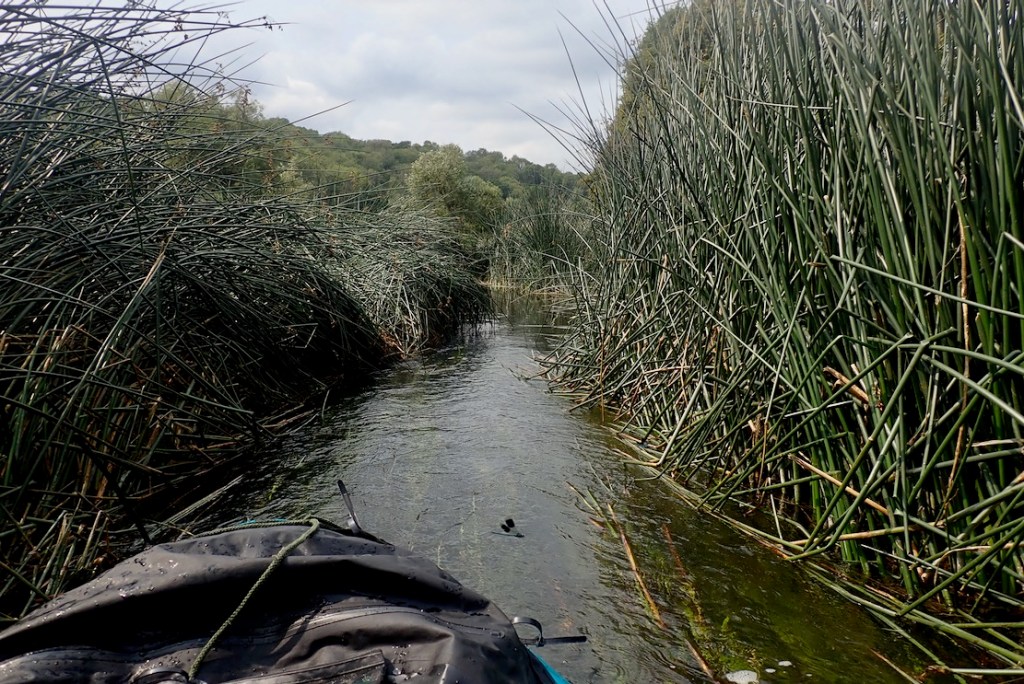
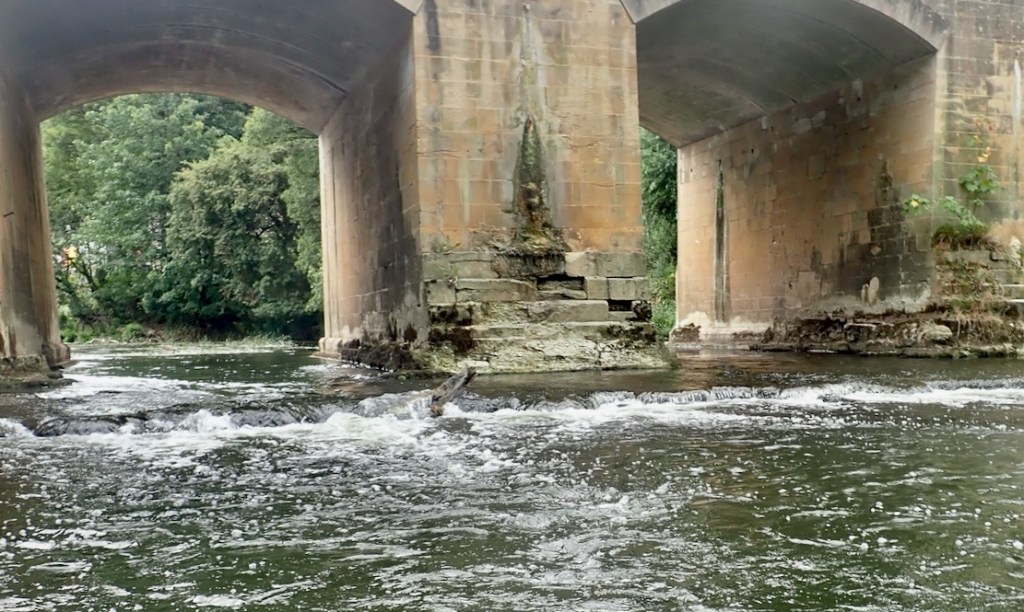
















Paddling along in the perfectly still water I had the feeling the boat was pulling to the left as if some weed was caught in the skeg or I wasn’t holding my paddle evenly. This wasn’t evident on the more lively river, earlier. I suspected I knew what it was: the skeg was warped, leaning over to one side and with a longitudinal curl at the back that would steer the boat left. I’ve not had this before on rock solid polyethylene skegs which don’t deform no matter how abused or badly packed. The unused one above with no tape or scratches is straight. I gave the bent one 2 minutes in a microwave but it came out the same. It is 3 years old from my original green TXL.
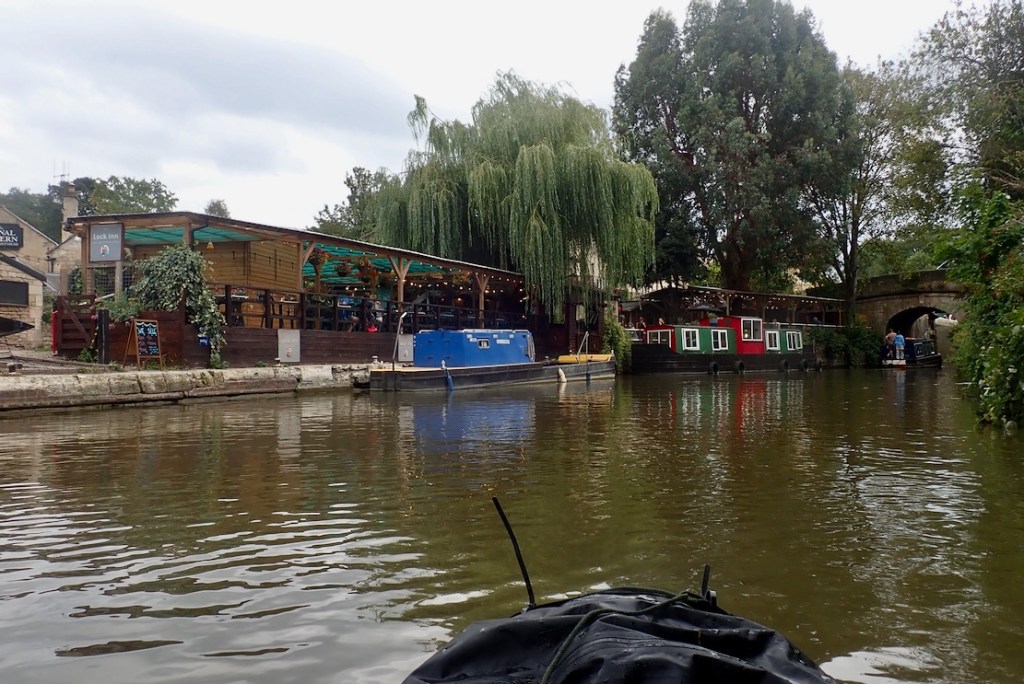


Unless you’re getting swept down Spain’s Canal de la Toba, as expected, the river stage was a lot more agreeable than the parallel canal, and the two weirs portaged were not awkward. At much higher (or normal?) flows that might be different but anyway, the whole point of packboats is you don’t need to do loops if there is transport at hand.
Had I thought it through a bit more, I’d have registered the railway also following the Avon valley, and carried on six miles down river. There are weirs at Warleigh, a mile after Dundas, and Bathampton, both of which would hopefully with no more bother than what passed before. They lead to Bath’s amazing, neo-classically set Pulteney Weir, doable providing it’s no more turbid than pictured below. Bath Spa station is just 5 minutes away for the 16-minute train ride back to Bradford on Avon, looking down onto the river you just paddled. One for next time.
Pulteney has had it’s share of tragedies, though the weir’s grim record must down to its city-centre location. The unusual V-shape actually only dates from the 1970s, replacing a diagonal low-head weir (above left), like most weirs upstream. Check out a great series of before-, during-, and after photos here, although the current log-jammed image on Google Earth doesn’t look inviting at all. They is actually a canoe chute alongside a dry ramp on the left hand end, by the trees. See this vid.